This algorithm is a variant for non-connected graphs.
Where:
- represents a node.
- represents the total number of nodes.
- represents the number of nodes in the same component as .
- represents another node The shortest distance from to .
Centrality algorithms are used to understand the influence of specific nodes in a graph and their impact on the network, which can help us identify the most important nodes.
This article will introduce the following algorithms:
Used to measure the number of relationships a node has. The larger the value, the higher its centrality.
G = ( V, E ).CD′(Ni)=n−1Ndegree
Where:
This formula has been standardized.
Used to discover nodes that can efficiently propagate information through subgraphs, The higher the value, the shorter the distance between it and other nodes. This algorithm can be used when you need to know which node has the fastest propagation speed.
G = ( V, E ).The indicator for measuring the centrality of a node is its average distance to other nodes. The closeness centrality algorithm calculates the sum of its distances to other nodes on the basis of calculating the shortest path between all node pairs, and then calculates the inverse of the result.
C(u)=∑v=1n−1d(u,v)1
Where:
It is more common to normalize the calculation result to represent the average length of the shortest path, rather than the sum of the shortest paths. The normalization formula is as follows:
Cnorm(u)=∑v=1n−1d(u,v)n−1
This algorithm is a variant for non-connected graphs.
CWF(u)=N−1n−1(∑v=1n−1d(u,v)n−1)
Where:
Used to detect the degree of influence of a node on the information flow or resources in the graph, usually used to find nodes that bridge one part of the graph with another.
G = ( V, E ).BC(v)=s=u=t∑σstσst(v)
Where:
In simple terms, betweenness centrality measures the node v by the proportion of the shortest paths between point pairs that pass through node v. Importance.
The following figure shows the steps to calculate the betweenness score.
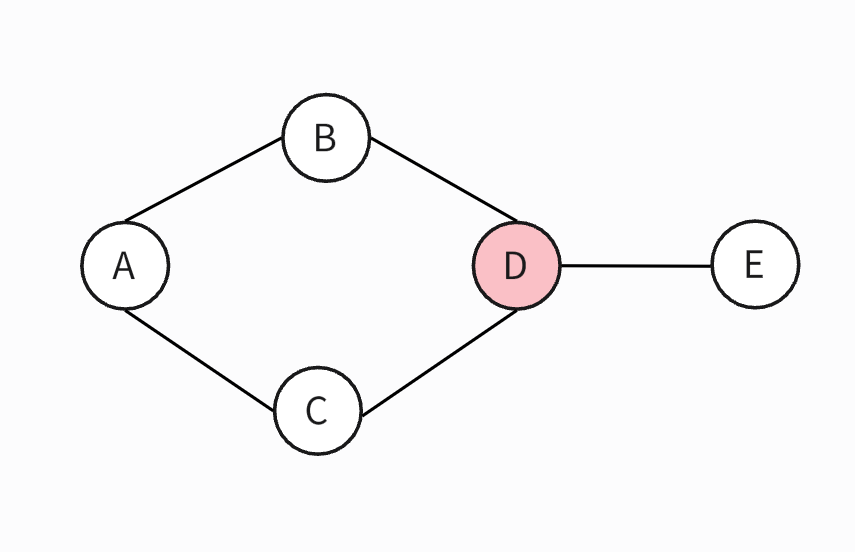
The calculation process for node D is as follows:
| Shortest path node pairs through D | Total number of shortest paths between node pairs p | Percentage of the number of shortest paths through D pp(u) |
|---|---|---|
| ( A, E ) | 1 | 1 |
| ( B, E ) | 1 | 1 |
| ( C, E ) | 1 | 1 |
| ( B, C ) | 2 ( B->A->C and B->D->C respectively ) | 0.5 |
So according to the formula, the betweenness score of node D is: 1 + 1 + 1 + 0.3 = 3.5.
Different from linear sequential programming calculations, the algorithm given here is based on Pregel's message propagation method for calculation. It is only for reference.
contribution=σstσsv×σvt
Suppose we have three nodes: source node s, intermediate node v and target node t. What we need to calculate is: the proportion of the path passing through node v to all shortest paths from s to t. The σsv×σvt in the formula is the number of shortest paths between s and t that pass through v, which is the combination principle of the shortest path from s to t. The shortest path of t is considered as the combination of the path from s to v and the path from v to t.
def calculate_betweenness_centrality ( source, all_nodes ) :
BC_s = 0
for t in all_nodes:
if t == source:
continue
for v in all_nodes:
if v == source or v == t:
continue
sigma_sv = get_shortest_path_count ( source, v )
sigma_vt = get_shortest_path_count ( v, t )
sigma_st = get_shortest_path_count ( source, t )
if sigma_st == 0:
continue
contribution = ( sigma_sv * sigma_vt ) / sigma_st
BC_s += contribution
return BC_sThis article introduces three different centrality algorithms, each of which identifies important nodes in the graph from different perspectives.
The importance of nodes is evaluated by calculating the in-and-out degree of each node. Nodes with high degree centrality mean that they are connected to more nodes.
The importance of nodes is measured by calculating the average distance to other nodes. Nodes with high closeness centrality mean a more central position in the graph, and the path from it to all other nodes is shorter, which will be faster if messages are propagated.
The importance of nodes is measured by calculating the probability that the shortest path between other nodes passes through itself. It is usually used to detect the degree of influence of nodes on information flow or resources in the graph. Nodes with high betweenness centrality mean that they are important bridges between two groups of nodes in the graph.
References for this article
941fa-feat(theme): upgrade and use collectionson eb6eb-improve(docs): use pangu formatteron 99791-fix(docs): image not shown due to image size settingon 25255-fix(docs): text typoon fea7c-improve(docs): delete extra whitespace and blank lineson de6ec-improve(docs): add summaryon 6176b-fix(docs): fix text typoon c11b4-fix(docs): optimize articleson cf762-feat(docs): add new english articleson Copyright Ownership:dingyuqi
License under:Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC-BY-NC-ND-4.0)