A Record of Troubleshooting a RocketMQ Message Duplicate Issue
On the last day of 2025, I'm recording a RocketMQ message duplicate delivery issue I encountered this year. Essentially, it was caused by incorrect Consumer parameter settings.

MySQL Composite Index Practical Guide
In the actual development process, it is inevitable to create composite indexes for MySQL. However, considering the leftmost matching principle and some index failure scenarios, there are still some tricks to create indexes. This article will give some simple scenarios and discuss how to create MySQL composite indexes most effectively based on these scenarios.
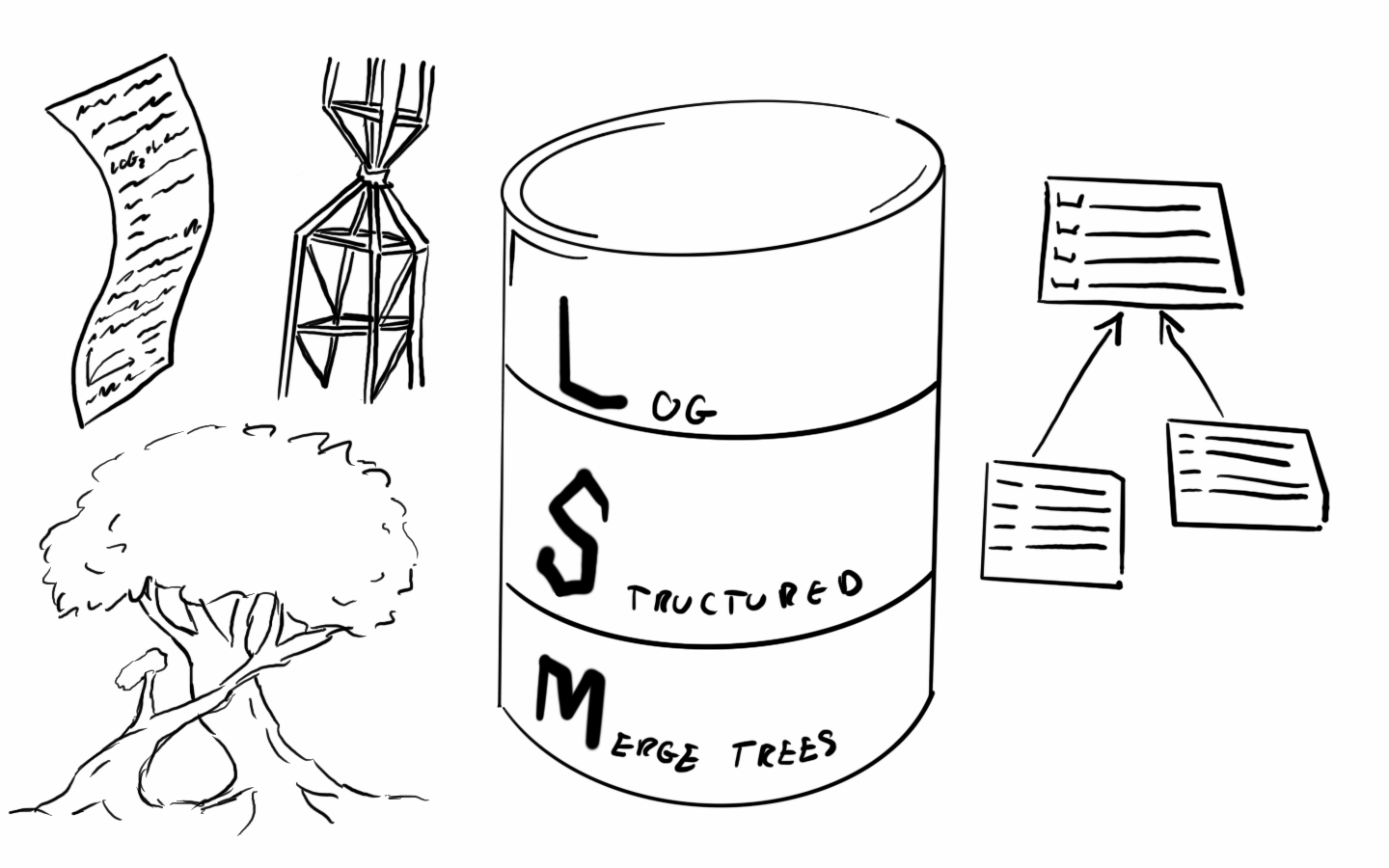
LSM-Tree: Learn about the core of NoSQL storage systems in one article
If you have ever been exposed to NoSQL databases, such as HBase, LevelDB, and RocksDB, then you should have heard of LSM trees. Most NoSQL databases have LSM trees at the bottom. The concept of LSM trees comes from a paper: The Log-Structured Merge-Tree ( LSM-Tree ). Today we will discuss the principles of LSM trees and how they add, delete, query, modify and merge data.

How to safely store user passwords in the backend? Add salt!
Almost all systems require users to register and log in, and the most common way to log in is to let users enter their username and password. Many early systems only required usernames and passwords to log in, but some websites have been attacked by brute force, social engineering refers to an attack method that manipulates human psychology rather than technical means to obtain passwords or sensitive information. The core is to exploit human weaknesses, such as trust, fear, curiosity or negligence, to induce the target to actively leak information or perform specific operations. refers to the data in the database being directly exported by the attacker.
How to reduce inventory under high concurrency?
This is a common scenario in e-commerce. Currently, Internet giants have very mature solutions for it. I wrote this article just to give some of my own thoughts.
MVCC Mechanism of MySQL Database
MySQL, as a multi-threaded database, supports concurrent queries from clients and sets its default isolation level to repeatable read. So how does MySQL isolate transactions in concurrent operations? It actually uses the
What is HDFS?
If you are also a big data worker, you must have heard of the distributed file system:
Overview of Fundation Models
With the development of the times, the application of foundation models in various fields is expanding. This article tries its best to sort out various materials and will give a brief overview of foundation models from the aspects of concept definition, type classification, training and application.
About Redis Persistence And Clustering
Redis is a very commonly used key-value database. The use of memory and HashMap for storage brings efficient queries. This article will introduce the persistence principle of Redis, the deployment method of clusters, and the expiration and elimination mechanism of key-value pairs.
Keep It Simple
Everything can be explained in one sentence.
ShenZhen, China